If the current model has parameters, then the value of these parameters may be set by modifying the text field in the middle region of the model panel.
The bottom region of the model panel includes a list of the names of the output variables. By changing the text fields in this regions, the user can compute level sets as the level is varied. For example, you may be interested in the level set f=c as c for different values of c.
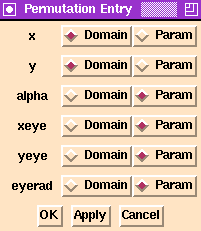
The Pisces Permutation Panel.
The "Permute" button will bring up the permutation panel. This panel allow users to exchange the role of domain variables and parameters. By choosing a variable to be in the domain, you are saying that you want Pisces to allow this function to vary while it computes the level set. Domain variables are sometimes called "active variables" whereas parameters are sometimes called "inactive variables."
![[Pisces]](../../../pix/pi.gif) The Pisces Home Page
The Pisces Home Page