The angle defect of a polyhedron
Next: Descartes's Formula.
Up: Geometry and the Imagination
Previous: Course projects
The angle defect at a vertex of a polygon is defined to be 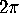 minus the sum of the angles at the corners of the faces at that vertex.
For instance, at any vertex of a cube there are three angles of
minus the sum of the angles at the corners of the faces at that vertex.
For instance, at any vertex of a cube there are three angles of 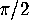 ,
so the angle defect is
,
so the angle defect is 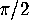 . You can visualize the angle defect by
cutting along an edge at that vertex, and then flattening out a neighborhood
of the vertex into the plane. A little gap will form where the slit is:
the angle by which it opens up is the angle defect.
. You can visualize the angle defect by
cutting along an edge at that vertex, and then flattening out a neighborhood
of the vertex into the plane. A little gap will form where the slit is:
the angle by which it opens up is the angle defect.
The total angle defect of the polyhedron is gotten by adding up the
angle defects at all the vertices of the polyhedron. For a cube,
the total angle defect is 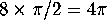 .
.
-
What is the angle sum for a polygon (in the plane) with
 sides?
sides?
-
Determine the total angle defect for each of the 5 regular polyhedra,
and for the polyhedra handed out.
Next: Descartes's Formula.
Up: Geometry and the Imagination
Previous: Course projects
Peter Doyle
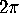 minus the sum of the angles at the corners of the faces at that vertex.
For instance, at any vertex of a cube there are three angles of
minus the sum of the angles at the corners of the faces at that vertex.
For instance, at any vertex of a cube there are three angles of 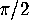 ,
so the angle defect is
,
so the angle defect is 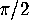 . You can visualize the angle defect by
cutting along an edge at that vertex, and then flattening out a neighborhood
of the vertex into the plane. A little gap will form where the slit is:
the angle by which it opens up is the angle defect.
. You can visualize the angle defect by
cutting along an edge at that vertex, and then flattening out a neighborhood
of the vertex into the plane. A little gap will form where the slit is:
the angle by which it opens up is the angle defect.
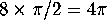 .
.
 sides?
sides?