 ,y
,y ,z
,z ):
):
Next: 10.2 Formulas for Symmetries in Homogeneous Coordinates
Up: 10 Space Symmetries or Isometries
Previous: 10 Space Symmetries or Isometries
In the formulas below, a multiplication between a matrix and a triple of coordinates should be carried out regarding the triple as a column vector (or a matrix with three rows and one column).
Translation by (x ,y
,y ,z
,z ):
):
(x,y,z)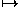 (x+x
(x+x , y+y
, y+y , z+z
, z+z )
)
Rotation through 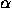 (counterclockwise) around the line
through the origin with direction cosines a, b, c
(see
(counterclockwise) around the line
through the origin with direction cosines a, b, c
(see ![]() ):
):
(x,y,z)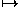 M(x,y,z),
M(x,y,z),
where M is the matrix
Rotation through 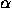 (counterclockwise) around the line
with direction cosines a,b,c through an arbitrary point (x
(counterclockwise) around the line
with direction cosines a,b,c through an arbitrary point (x ,y
,y ,z
,z ):
):
(x,y,z)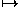 (x
(x ,y
,y ,z
,z )+M(x-x
)+M(x-x ,
y-y
,
y-y , z-z
, z-z ),
),
where M is given by (1) .
Arbitrary rotations and Euler angles. Any rotation of space
fixing the origin can be decomposed as a rotation by 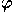 about the
z-axis, followed by a rotation by
about the
z-axis, followed by a rotation by 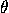 about the y-axis,
followed by rotation by
about the y-axis,
followed by rotation by 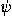 about the z-axis. The numbers
about the z-axis. The numbers
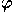 ,
, 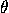 and
and 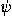 are called the Euler angles of the
composite rotation, which acts as follows:
are called the Euler angles of the
composite rotation, which acts as follows:
(x,y,z)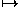 M(x,y,z),
M(x,y,z),
where M is the matrix given by
(An alternative decomposition, more natural if we think of the
coordinate system as a rigid trihedron that rotates in space, is the
following: a rotation by 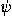 about the z-axis, followed by a
rotation by
about the z-axis, followed by a
rotation by 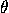 about the rotated y-axis, followed by a
rotation by
about the rotated y-axis, followed by a
rotation by 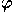 about the rotated z-axis. Note that the
order is reversed.)
about the rotated z-axis. Note that the
order is reversed.)
Provided that 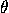 is not a multiple of
180°, the
decomposition of a rotation in this form is unique (apart from the
ambiguity arising from the possibility of adding a multiple of
360°to any angle). Figure 1 shows how the
Euler angles can be read off geometrically.
is not a multiple of
180°, the
decomposition of a rotation in this form is unique (apart from the
ambiguity arising from the possibility of adding a multiple of
360°to any angle). Figure 1 shows how the
Euler angles can be read off geometrically.
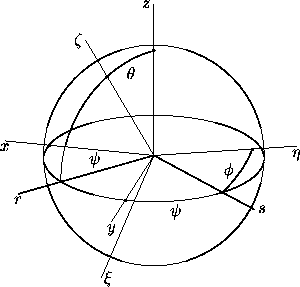
Figure 1: The coordinate rays Ox, Oy, Oz, together with their images
O , O
, O , O
, O under a rotation, fix the Euler angles associated
with that rotation, as follows:
under a rotation, fix the Euler angles associated
with that rotation, as follows:
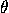 =zO
=zO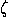 ,
, 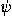 =xOr=yOs, and
=xOr=yOs, and 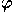 =sO
=sO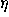 . (Here
the ray Or is the projection of O
. (Here
the ray Or is the projection of O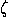 to the
xy-plane. The ray Os is determined by the intersection of the
xy- and
to the
xy-plane. The ray Os is determined by the intersection of the
xy- and 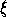
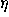 -planes.)
-planes.)
Warning. Some references define Euler angles differently; the most common variation is that the second rotation is taken about the x-axis instead of about the y-axis.
Screw motion with angle 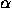 and displacement d around the line
with direction cosines a, b, c through an arbitrary point (x
and displacement d around the line
with direction cosines a, b, c through an arbitrary point (x ,y
,y ,z
,z ):
):
(x,y,z) (x
(x +ad, y
+ad, y +bd, z
+bd, z +cd) + M(x-x
+cd) + M(x-x , y-y
, y-y , z-z
, z-z ),
),
where M is given by (1) .
Reflection
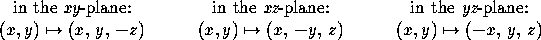
Reflection in a plane with equation ax+by+cz+d=0:
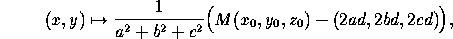
Reflection in a plane going through (x ,y
,y ,z
,z ) and whose
normal has direction cosines a, b, c:
) and whose
normal has direction cosines a, b, c:
(x,y) (x
(x +y
+y +z
+z )+M(x-x
)+M(x-x , y-y
, y-y ,
z-z
,
z-z ),
),
where M is as in (3) .
Glide-reflection in a plane P with displacement vector v: Apply first a reflection in P, then a translation by the vector v.
![[HOME]](/pix/home.gif) The Geometry Center Home Page
The Geometry Center Home PageSilvio Levy
Wed Oct 4 16:41:25 PDT 1995
This document is excerpted from the 30th Edition of the CRC Standard Mathematical Tables and Formulas (CRC Press). Unauthorized duplication is forbidden.